Power of LED lamps table. Comparison of incandescent, compact fluorescent and LED lamps by luminous flux
Hello, dear readers and guests of the Electrician's Notes website.
Due to the wide range of lamps, people often have the question of which lamps to choose?
Some citizens still use incandescent lamps (LN), although their use is limited by Federal Law No. 261 "On Energy Saving", someone finally switched to compact fluorescent lamps(CFL), and someone is already content with LED lamps (LED).

So what to choose? I often have to answer this question, so I decided to write a few articles where I will compare an incandescent lamp, a compact fluorescent lamp (CFL) and led lamps s (LED) among themselves according to the following criteria:
- luminous flux at different voltage levels
- lamp ignition time
- heating temperature of the body and flask in operating mode
- actual power consumption (energy consumption)
For the experiment, I will take an incandescent lamp with a power of 75 (W), its equivalent is a compact fluorescent lamp (CFL) with a power of 15 (W) "Navigator" ("Navigator") and a light-emitting diode lamp (LED) with a power of 9 (W) EKF series FLL-A.
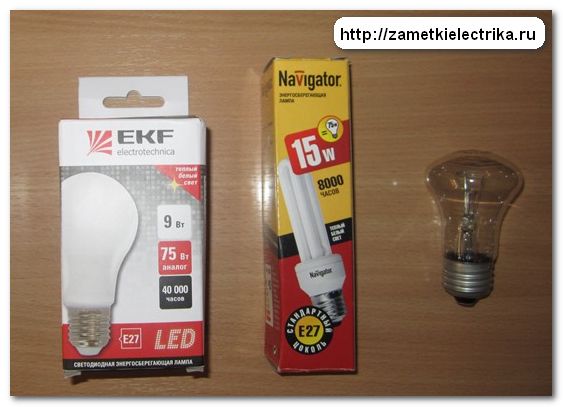

All lamps have a standard E27 base.
I picked up the lamps with the same declared parameters of the luminous flux and color temperature.
The declared characteristics of the lamps (according to the passport)

Characteristics of the incandescent lamp:
- rated lamp power - 75 (W)
- mains voltage - 230-240 (V)
- luminous flux - 935 (lm)
- luminous efficiency - 12.5 (Lm / W)
- color rendering index Ra - 100
- service life - 1000 (hours)
- environmental friendliness - does not contain mercury and other harmful substances
- dimensions (diameter, height) - 50 x 88 (mm)
I calculated the luminous efficiency by dividing the luminous flux (according to the passport) by the rated power of the lamp.

Incandescent lamps are fully compatible with light control equipment (), electronic switches (for example), various, etc.
2. Compact fluorescent lamp (CFL) with a power of 15 (W) "Navigator"

Here are its characteristics:
- rated lamp power - 15 (W), analogue of a 75-watt incandescent lamp
- mains voltage - 220-240 (V)
- color temperature - 2700 (K) warm white light
- luminous flux - 1000 (lm)
- luminous efficiency - 66.6 (Lm / W)
- service life - 8000 (hours)
- operating temperature — from -25°С to +40°С
- environmental friendliness - contains mercury vapor
- dimensions (diameter, height) - 38 x 151 (mm)
The CFL lamp is not compatible with dimming devices, electronic starters and light sensors.



Has the following characteristics:
- lamp rated power - 9 (W), equivalent to a 75-watt incandescent lamp and a 15-watt CFL lamp
- mains voltage - 170-240 (V)
- color temperature - 2700 (K) warm white light
- luminous flux - 800 (Lm)
- luminous efficiency - 88.8 (Lm / W)
- color rendering index Ra - more than 82
- dispersion angle — 240°
- service life - 40000 (hours)
- environmental friendliness - does not contain mercury and other harmful substances
- absence of ultraviolet and infrared radiation
- dimensions (diameter, height) - 60 x 110 (mm)
- warranty - 2 years

light diode lamp(LED) EKF series FLL-A is not compatible with dimmers, electronic switches and other similar devices.

Let me tell you a few words about this lamp.
To date, LED lamp EKF series FLL-A is a novelty in the market of lighting products. Manufacturers confidently declare that it has advantages over LED lamps from other companies.
Firstly, the EKF FLL-A series has a special composite housing made of aluminum and heat-dissipating plastic, which provides good heat dissipation, which means it increases the lamp life (in this case, up to 40,000 hours). If you turn on the lamp for only 3 hours a day, then theoretically it should last for 36.5 years.
Let me remind you that the service life of an LED lamp ends when its luminous flux has decreased by more than 30% of the original.

Secondly, it uses high-efficiency SMD LEDs from the Epistar brand (Taiwan), which allow you to achieve a high level of light power - in my example up to 88.8 (Lm / W).
By the way, the EKF lamp of the FLL-A series has the usual shape and dimensions, commensurate with an incandescent lamp (LN). Also, the light flux has a dispersion of 240 degrees, which is very pleasing.

Luminous flux (illuminance) of incandescent, CFL and LED lamps
Luminous flux is one of the main parameters for lamps, which can be used to analyze the power of light (radiation) perceived by a person. It is measured in "lumens" (Lm).
Illuminance is the ratio of the value of the luminous flux of the lamp to the area of the illuminated surface. It is measured in "lux" (Lx). It is by the magnitude of illumination that the intensity of illumination of a particular lamp at different points on the surface is determined.
1 Lk \u003d 1 Lm / 1 sq.m, i.e. the illumination on the surface is 1 (Lx) if the luminous flux with a power of 1 (Lm) falls on a surface with an area of 1 (sq.m.)
Each type of premises, whether industrial or domestic, has its own standards and requirements for illumination (see SNiP 23-05-95 "Natural and artificial lighting").
In my experiment, I will measure the illumination on the desktop surface at one point (strictly in the center of the axis) from a lamp rigidly fixed to the same table. The distance from the lamp to the table surface is 65 (cm).

I know that according to the method, illumination is measured somewhat differently and at different points, but other things being equal, this will be quite enough for me.
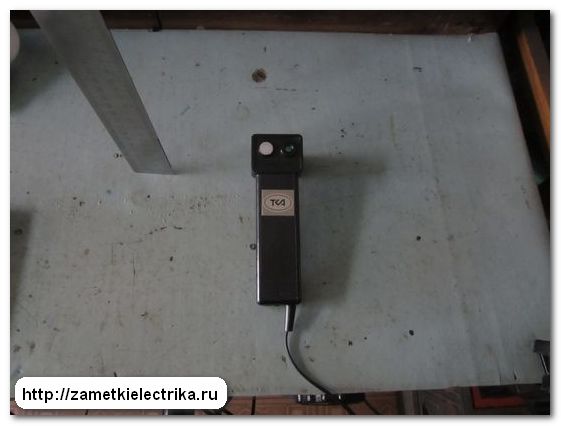
As a light meter, I use a digital photometer (light meter - luminance meter) TKA - 04/3. This is how it looks.
![]()
The essence of the measurement is as follows. I will alternately screw the lamps into the lamp and measure the illumination on the surface of the table.
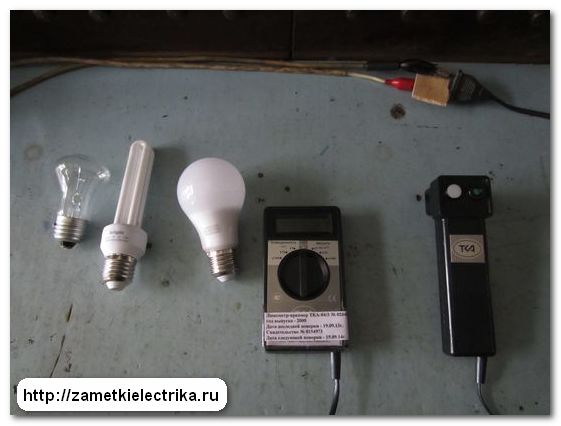

Measurement of illumination at a nominal voltage of 220 (V)
First, I will measure the illumination on the table surface from each lamp at a nominal supply voltage of 220 (V).
I'll start with a 75 (W) incandescent lamp.
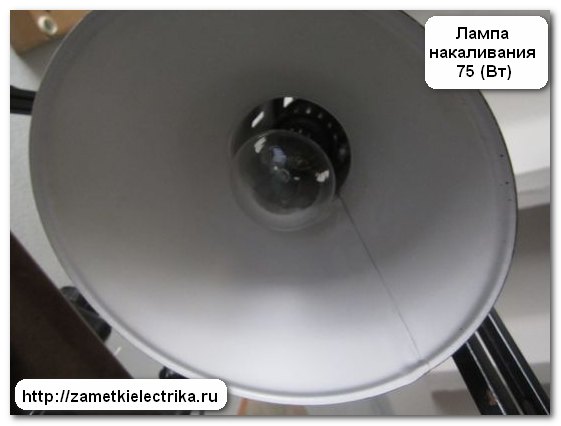

I screw it into the lamp and with the help of a luxmeter I fix the value of its illumination. It turned out 560 (Lk).

The next CFL lamp "Navigator" with a power of 15 (W), presented as the equivalent of a 75-watt incandescent lamp.

Her result was about 389 (Lk).
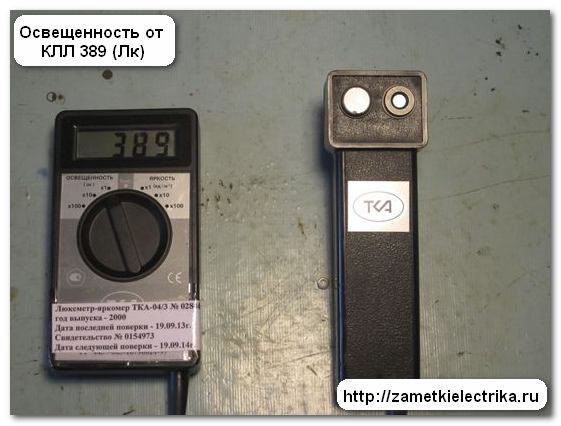

The EKF FLL-A LED lamp with a power of 9 (W), presented as an analogue of the 75-Watt incandescent lamp, showed a result of 611 (Lx).
![]()


Measurement of illumination at reduced voltage 180 (V) and 198 (V)
I am currently interested in how the luminous flux of the lamps will change with a decrease in the supply voltage. Let's check!!!
With the help of a laboratory autotransformer (LATR), I will reduce the supply voltage to 198 (V). This is just the lower limit of the maximum allowable voltage from 220 (V).
Illumination from an incandescent lamp 75 (W) at a voltage of 198 (V) was 313 (Lx).

Illumination from a compact fluorescent lamp "Navigator" 15 (W) at a voltage of 198 (V) was 336 (Lx).

The illumination from the LED lamp EKF 9 (W) at a voltage of 198 (V) was 611 (Lx).

For the interest of the experiment, I will reduce the mains voltage to 180 (V). Let's see how the lamps behave.
Illumination from an incandescent lamp 75 (W) at a voltage of 180 (V) was 224 (Lx).

Illumination from a compact fluorescent lamp "Navigator" 15 (W) at a voltage of 180 (V) was 313 (Lx).

The illumination from the LED lamp EKF 9 (W) at a voltage of 180 (V) was 611 (Lx).

In principle, everything is clear with an incandescent lamp and a fluorescent lamp, their luminous flux decreases depending on the level of reduced voltage. But pay attention to the EKF LED lamp of the FLL-A series. Its luminous flux remains unchanged regardless of voltage reduction.
It became interesting to me and I lowered the voltage to 130 (V). Look at the result.
![]()
It's just stunning! Even at 130 (V), the luminous flux of the lamp corresponds to luminous flux, as in rated voltage 220(B).
Measurement of illumination at increased voltage 242 (V)
Now, on the contrary, we increase the voltage of the network. Using the same laboratory autotransformer (LATR), I will increase the voltage to 242 (V). This is just the upper limit of the maximum allowable voltage of 220 (V).
Here are the results.
Illumination from an incandescent lamp 75 (W) at a voltage of 242 (V) was 666 (Lx). What is the "magic" number.
![]()
Illumination from a compact fluorescent lamp (CFL) "Navigator" 15 (W) at a voltage of 242 (V) was 405 (Lx).


For clarity, the results obtained for illumination from the considered lamps at different voltage levels, I entered in one general table:
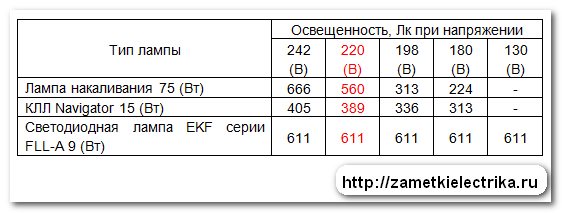
From the results obtained, the following conclusions can be drawn:
1. An incandescent lamp 75 (W), with a decrease in the supply voltage, significantly reduces its luminous flux. For example, when the supply voltage is reduced by 10% (198 V), the illumination from the lamp decreases by 44%, and when the voltage is reduced by 18% (180 V), the illumination from the lamp decreases by 60%. Conversely, with an increase in the supply voltage by 10% (242 V), the illumination from the lamp increased by 19%.
2. Compact fluorescent lamp "Navigator" 15 (W) was claimed to be equivalent to a 75-watt incandescent lamp, but at a nominal voltage of 220 (V) it is significantly inferior in illumination by as much as 30%. Although according to the passport, its luminous flux was declared the most - 1000 (Lm) against 935 (Lm) incandescent lamps and 800 (Lm) LED lamps.
It turns out that the considered CFL "Navigator" 15 (W) is not the equivalent of a 75-watt incandescent lamp, as stated in the passport. Most likely it corresponds to a 40-watt or 60-watt incandescent lamp.
Unfortunately, this is not news to me.
I often hear that they replaced all the incandescent lamps in the apartment with CFLs (power equivalence was observed), and the apartment became “dark”. Here, this experiment confirms my assumptions, so when buying CFL lamps, do not forget about this nuance.
Also, in CFLs, when the supply voltage changes, a change in the luminous flux is observed, but somewhat less than that of an incandescent lamp. For example, with a decrease in the supply voltage by 10% (198 V), the illumination decreased by about 13.5%, and with a decrease in voltage by 18% (180 V), the illumination decreased by 20%. Conversely, with an increase in the supply voltage by 10% (242 V), the illumination from the lamp increased by only 4%.
3. LED lamp (LED) EKF series FLL-A in this experiment showed its best side.
Firstly, it has the best value in terms of desktop illumination - 8% more than an incandescent lamp, and 36% more than a CFL.
Secondly, when the supply voltage changed from 130 (V) to 242 (V), the illumination of the desktop did not change at all - it remained at the same level. Manufacturers claim that the driver used in this lamp stabilizes the luminous flux, regardless of the decrease or increase in voltage. And this is clearly confirmed in the experiments.
Ignition time for incandescent, fluorescent and LED lamps
We already know the illumination of the working surface from the lamps from the first experiment. Therefore, now we will measure the time of full ignition of the lamps to 100% of the luminous flux, i.e. determine the time after which the lamp will reach the nominal operating mode.
Results:
- incandescent lamp 75 (W) - instantly
- CFL "Navigator" - 2 minutes
- light-emitting diode lamp (LED) EKF - instantly
As you can see, in this experiment, the Navigator compact fluorescent lamp is inferior to everyone. Its ignition time was more than 2 minutes.
For incandescent lamps and EKF LED lamps, the luminous flux from the first seconds reaches the nominal operating mode.
Color temperature and color rendering index LN, CFL and LED
Color temperature is the wavelength of a light source in the optical range. Measured in Kelvin.
A few examples: 1500-2000 (K) - candle flame, 2000 (K) -, 3400 (K) - sun at the horizon, 7500 (K) - daylight.
Color rendering is the visual perception of the same object illuminated by the light source under study (in my case, it is an incandescent lamp, CFL and LED), compared to a reference light source (the Sun or a completely “black body”). Dimensionless value.
According to passport data, the color temperature of all three lamps is 2700 (K) - warm white light. The color rendering index for an incandescent lamp is Ra = 100, for CFLs - Ra = 70-80, and for LEDs - Ra = 82.
I don’t have special equipment (spectrophotometer) for measuring color temperature and color rendering index, so we’ll limit ourselves to a visual comparison.

In any case, objects illuminated by an incandescent lamp will have more natural colors than with CFL or LED.
Video for this article:
P.S. To be continued ... In the next article, using a thermal imager, I will measure. Don't miss out - subscribe to the newsletter.
The increase in the cost of electricity leads to the need to find ways to reduce its consumption. A significant part of it is spent on lighting, where the incandescent lamp prevailed as a light source for a long time. Now there are more economical light sources. Here the main indicator is the power of energy-saving lamps. A table of their comparison with conventional lamps is given in advertisements or in comparative characteristics.
An incandescent lamp consists of a sealed bulb filled with an inert gas, with a tungsten filament inside. When passing through electric current glow is produced. Up to 90% of the electricity here goes into heat. However, it does not last long and has a small light output.
The light output and color rendering of an incandescent lamp has been increased by adding halogen vapors to inert gases. At the same time, its principle of operation remained the same, but decreased by 40%.
Fluorescent lamps
As an alternative light source, it has long been used (LL), the efficiency of which is 70%. It consists of a sealed glass tube filled with an inert gas and mercury vapor. Inside, a layer of phosphor is applied to the surface of the glass, which begins to glow when the lamp is ignited from the ballast. In everyday life, the use of LL is not very convenient, as a result of which they were made more compact by placing the starting device inside the base. Due to this, the lamp can work together with standard cartridges. As a result, it can be installed instead of a conventional incandescent lamp without altering the lamp, which is an advantage. It is important to correctly determine what voltage it is designed for.
The compact fluorescent lamp is called an energy-saving lamp (ECL) and has become widely used.
Characteristics of energy-saving lamps
The efficiency of all types of lamps is evaluated according to the following indicators.
- Power - the amount of electricity consumed in one hour, W.
- Luminous efficiency - the amount of light per 1 watt expended, Lm / W. The power of the luminous flux of energy-saving lamps is 5 times greater than that of standard light sources.
- Color rendering index - the level of correspondence between the apparent and natural colors of the illuminated body%.
and power
Fluorescent lamps at first were created without standards, since they were used mainly as illuminated advertisements, where each product was different from the others. Their use as lighting fixtures has led to the need to group by characteristics so that they can be matched to the appropriate electrical wiring or luminaire. The main properties of the lamps can be determined by marking. 
The first letter of the domestic marking reflects the color: B - white, U - universal, D - daylight, C - improved color rendering, etc.
The international marking indicates the color code, where the first digit reflects the color rendering index (for the house it should be equal to 8), and the remaining two - the color temperature in hundreds of degrees (827, 830, 836 are used for the house).
Bases are designated E40 (for powerful (standard), E14. (smaller diameter - 14 mm).E14 energy-saving lamps are designated with a base diameter of 14 mm. 
For ESL, pin bases are often used: 2D, G23, 2G7, GU, etc.
Power is indicated in watts before the letter W. A common is an 11w energy-saving lamp with screw and pin bases. 
ECLs with soft start are designated RS.
Lamp voltage is indicated in volts: 12 V, 126 V, 220 V.
The ESL marking usually indicates all the main parameters. Some manufacturers may have a different location, but it's easy to figure it out.
LED lamp
Another new energy-saving light source is the LED lamp, which has created a real breakthrough in energy efficiency. It allows you to further reduce energy consumption, as well as improve light output, increase service life and improve fire safety. All these qualities are provided by the built-in matrix, which is a series of LEDs connected in series. The intensity of light depends on their number.
Comparison of energy saving lamps and incandescent lamps
Traditionally, lamps are selected by power, but now it would be more correct to evaluate them by luminous flux, since the illumination of the room depends on it. 
The consumer is accustomed to evaluating the illumination by the power of incandescent lamps. Therefore, it is convenient for him to evaluate the power of energy-saving lamps (table) by equal illumination created by different types of light sources. 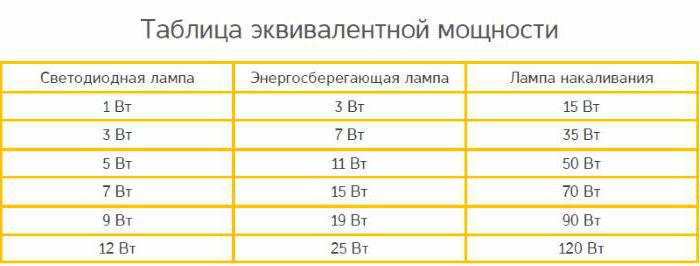
The table clearly shows the dependence of power consumption on the type of light source. It is obvious here that ESLs have significantly lower power at the same brightness as an incandescent lamp. However, for different manufacturers, the brightness may differ significantly from the declared one. In addition, the amount of light depends on the volume of the bulb: the smaller it is, the lower the luminous flux. When choosing an ESL in a store, it should be evaluated according to the declared characteristics, the size of the flask and amended in the direction of increasing the stock. In addition, it must be taken into account that the incandescent lamp creates uniform illumination in all directions, while the LED has a directional flow. If a diffuser is installed on it, it takes some of the power.
The spectrum of the lamp is of no small importance. With an increase in brightness, the power consumption for creating the same luminous flux decreases.
ESL choice
Energy-saving lamps are selected according to their characteristics. The easiest way to estimate the required power of energy-saving lamps. A comparison table with other types of lamps is in any store. The power of the ESL should be 5 times less than that of an incandescent lamp. For example, instead of a 100-watt standard lamp, a 20-watt energy-saving lamp can be used. 
The light spectrum of all bulbs should be the same tone. In living rooms, soft tones (warm glow) are preferred.
The size and shape of the lamp depends, first of all, on the type of cartridge and the permissible dimensions of the lamp. The cheapest light bulbs are U-shaped, while the spiral ones are more expensive. Standard sizes are usually suitable for large chandelier shades or floor lamps. For small sconce caps, compact E14 energy-saving lamps are selected.
Sometimes new ESLs blink, which may be due to the presence of a backlight in the switch. Then you should remove the indicator from it or purchase an LED or halogen lamp. From low-quality goods, you must immediately refuse, and purchase a product of guaranteed quality, despite the higher price.
Dimmers
The brightness of standard lamps is adjusted by changing the power. When it decreases to the value of PD (dimming threshold), the light bulb turns off. For all types of lamps, except for fluorescent ones, the PD is close to zero and there are no problems with dimming.
ESL dimming
For ESL, combustion is maintained at a power of at least 10% of the nominal value, but to start the dimmer must be set to a level of at least 30%, and after the lamp is turned on, it can be reduced.
It is advisable to use on triacs, without current rectification, which makes it possible to save on the absence of power losses from diode bridges. Despite this, the dimmer is an additional burden. In addition, from "cold starts" fluorescent lamps fail faster. The dimming depth of ordinary lamps is very low, and to expand it and provide the necessary margin of safety, you should buy special expensive lamps with special electronic filling.
Dimming LED lamps
The LED lamp changes brightness depending on the amount of passing current. For it, there is an optimal mode in which the light output is maximum. Here it must be borne in mind that when the power changes, the shade of the glow changes accordingly. To keep it the same, dimmable LED lamps and dimmers are used to maintain a constant current amplitude with a change in the pulse current step. Naturally, this is reflected in the price increase.
Manufacturers try to produce products that best meet the needs of consumers. Philips has released lamp models that work normally with conventional dimmers.
Conclusion
Energy-saving lamps with guaranteed quality meet the declared parameters and provide energy savings when used correctly. You can easily choose the power of energy-saving lamps, the table of correspondence of which to typical incandescent lamps is attached everywhere for comparison. Dimmable lamps and compatible dimmers should be used to enable room lighting control.
– modern light sources that differ:
- long service life;
- environmental friendliness;
- high light output with low power consumption;
- mechanical and fire safety.
To choose the right power and number of lamps, you need to figure out how bright this or that product will shine. This is important for the implementation of comfortable visibility in the room, the selection of a light bulb for each device, taking into account the restrictions established by the manufacturer.
Features of power calculation
LEDs require an order of magnitude less energy than incandescent lamps. But for many buyers it is more convenient to navigate based on the ratio of the power of these two types of lighting.
The first value is indicated in W for conventional light bulbs, the second for LED bulbs, the luminous flux in Lumens is given in brackets:
Correspondence table for incandescent and LED lamps
When switching from fluorescent (energy-saving) to diode lighting, the comparative parameters will be as follows:
Correspondence table for fluorescent (energy-saving) and LED lamps
These parameters take into account the decrease in brightness due to the frosted bulb of the lamp, the energy consumption for heating the internal driver of the device. It should be borne in mind that the luminous intensity depends on the parameters of the base. The given average values are for products with E27 base. When choosing an LED, you should rely not only on power, but also on the strength of illumination.
In order for the product to serve for a really long time, and its brightness to meet expectations, you should choose lamps from well-known manufacturers that guarantee product quality. Unscrupulous manufacturers often indicate the wrong ratio of brightness to power on the packaging, misleading consumers. We sell only proven high-quality light bulbs that will illuminate your home or office for years to come.
Despite the fact that the cost of a diode product is somewhat higher compared to other options, such an investment is fully justified by significant energy savings, no flicker, and the possibility of mounting next to stretch ceilings.
Lighting standards
In order to calculate the optimal power and the required number of lamps, it is important to understand the accepted standards for a comfortable flow of light. The psychological and physical well-being of a person, his performance, interior aesthetics depend on this. Keep in mind that the perception of brightness depends on the color scheme in which the light flux is colored. Experts recommend shades that are closest to daylight. For precise operations, such as drawings or sewing, it is worth choosing whiter colors.
When creating a comfortable homely atmosphere, you can not do without lamps of a warm shade. For home and office space, it is not recommended to choose colorful extravagant options: blue, orange, green.
Only a specialist can create an accurate lighting project, but, focusing on existing standards, you can choose a fairly comfortable combination of lamps. Values are in watts per square meter:
- calm subdued level (bedroom) 1.5-2;
- average brightness level (nursery, bathroom, hallway, office, kitchen) 2-3;
- the highest power level (living room, office and administrative premises) 2.5-3.5.
These parameters are to be used as a guide and can be changed according to your preferences. In addition, we mean the bulbs of the central ceiling fixture with a ceiling height of not more than 3 meters. A little more LED lamps of low power will be needed for local fixtures.
With the active use of zonal devices, it is permissible to use upper LED lamps of lower power. If the ceiling height is more than 3 meters, the indicated source brightness standards should be multiplied by at least 1.5 times. For an office, nursery and kitchen, it is desirable to install lamps (sconces, table, built-in or pendant), where the lamp will act as additional light.
Due to the fact that the diode lamp has not only more power, but is also equipped with a frosted bulb, it evenly scatters the rays, therefore it is suitable for use with any type of ceiling lamps. As electricity consumption becomes less, it is permissible to slightly increase the performance of LED lamps in order to ensure a comfortable atmosphere. As in the case of high ceilings, the performance of LED products should be increased for interiors decorated in dark colors.
When looking for a light bulb, always make sure that the base of a particular electrical appliance and the product you are purchasing match. Using these simple rules, you can ensure a comfortable atmosphere at home or workplace.
